Introduction: Setting the Stage for Europe’s 2026 Economy
As Europe steps into 2026, a straightforward question hangs in the air: can economic resilience outpace global uncertainty?
The answer, for now, is cautiously optimistic.
After years of shocks, from energy crises to supply chain strain, Europe enters 2026 on steadier ground. Growth is modest, but momentum is real. Most forecasts point to Eurozone GDP growth of around 1.1 to 1.5 percent in 2026, driven by easing inflation, gradual wage gains, and targeted public investment. It’s not a boom year. But it is a rebuilding one.
Several forces will shape Europe’s economic horizon. Geopolitical tensions remain a wild card, especially for trade and energy. Parts of the continent still face deindustrialization pressures, rising costs, and aging workforces. Germany, long Europe’s growth engine, is rethinking its industrial model. Southern and Eastern Europe are pushing to catch up faster.
At the same time, opportunity is spreading.
Green technology, clean energy, and digital infrastructure are moving from policy goals to fundamental economic drivers. EU-backed investment is flowing into renewables, batteries, AI, and transport. Countries like Spain, Poland, and Bulgaria are seeing renewed interest from investors and employers. For workers and entrepreneurs, this shift is opening new doors.
This article is designed to help you read the signals clearly. Whether you’re planning investments, considering a move, running a business, or simply booking future travel, Europe’s economy in 2026 will affect your decisions.
The year ahead is not about quick wins. It’s about clever positioning.
Europe’s challenges are real, but so are its tools to face them. And for those paying attention, 2026 could be a pivotal year to act.
Europe’s Economic Overview: 1.3% GDP Growth Projection – A Stable but Cautious Path Forward
Europe’s economy in 2026 is expected to move forward, not quickly, but steadily. Current forecasts point to average GDP growth of around 1.3 percent, reflecting a continent that has regained balance after years of disruption. The recovery is uneven, but it is no longer fragile.
EU GDP growth forecast for 2026 shows modest expansion.
— Jack Prandelli (@jackprandelli) January 7, 2026
Highest growth:
– Malta: 3.8%
– Poland: 3.5%
– Lithuania: 3%
Strong performers (>2.5%):
Finland, Spain, Romania, Cyprus.
Lowest growth:
– Ireland: 0.2%
– Italy: 0.8%
Most countries cluster between 1–2.5%, with Northern… pic.twitter.com/oEtzKLQyte
At the Eurozone level, growth is projected closer to 1.1 percent, held back by weak external demand and slower global trade. Foreign demand for European goods is forecast to rise by just 1.9 percent in 2026, a reminder that Europe cannot rely on exports alone. Instead, domestic investment and policy support are doing more of the heavy lifting.
Growth is also shifting geographically. Germany is expected to regain momentum as fiscal stimulus, infrastructure spending, and industrial investment kick in. This partially offsets softer growth in parts of southern Europe, where tourism has peaked, and public finances remain tight. Eastern Europe, meanwhile, continues to benefit from EU funding and manufacturing relocation.
Inflation is no longer the dominant threat. Price pressures have cooled across most of the bloc, giving households more breathing room and allowing central banks to step back from aggressive tightening. That stability matters. It supports consumer confidence, long-term planning, and cross-border investment.
GDP growth outlook for 2026 (approximate forecasts):
| Region | GDP Growth 2026 |
|---|---|
| Eurozone (average) | ~1.1% |
| Germany | ~1.4% |
| France | ~1.2% |
| Southern Europe (avg.) | ~1.0% |
| United Kingdom | ~1.3% |
Key forces shaping Europe’s economy in 2026:
- AI and automation are improving productivity in manufacturing and services
- Targeted fiscal spending, especially in energy and infrastructure
- Trade uncertainty, linked to geopolitics and slower global growth
While growth remains modest, targeted reforms and investment offer clear bright spots. Europe is not racing ahead—but it is moving with purpose, and with more resilience than many expected.
Milestone Moment: Bulgaria’s Eurozone Entry on January 1, 2026 – Boosting Integration and Trade
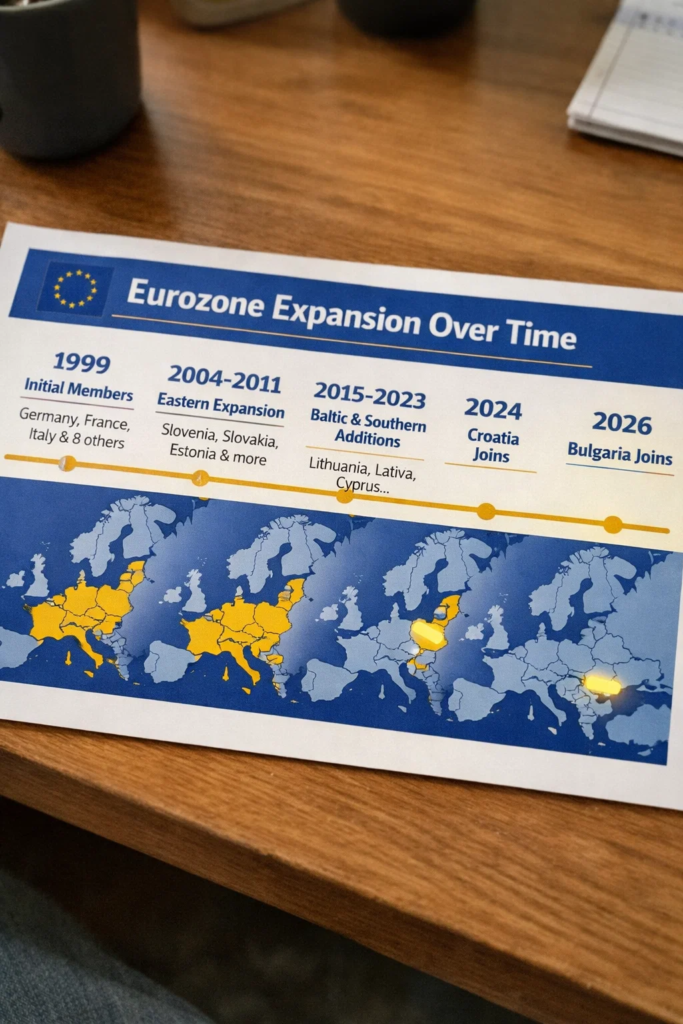
On January 1, 2026, Bulgaria is set to take a historic step. The country plans to adopt the euro, becoming the 21st member of the eurozone and formally replacing the lev at a fixed conversion rate. For the EU’s poorest member state, this move marks a significant leap toward deeper economic integration.
The impact goes well beyond symbolism.
For businesses, joining the eurozone removes currency risk overnight. Cross-border trade becomes simpler and cheaper. Contracts no longer need hedging against exchange swings. Payments across the bloc speed up. For a country closely tied to EU supply chains, that stability matters.
Tourism and investment are also expected to benefit. A shared currency makes Bulgaria easier to compare, cheaper to market, and more familiar to visitors. Investors often see euro adoption as a stamp of credibility, especially in banking and real estate. With Bulgaria already attracting manufacturing and outsourcing projects, the timing is strategic.
At a European level, the move expands the eurozone’s reach to more than 350 million people, reinforcing the currency’s role as a global anchor. It also strengthens economic links between Western Europe and the EU’s eastern edge.
Still, challenges remain. Public support in Bulgaria is mixed, driven by fears of price hikes and loss of control. Past euro adopters saw short-term inflation bumps, even when long-term effects proved modest. Clear communication and price monitoring will be critical in the first year.
What euro adoption means in practice:
For businesses
- No currency conversion costs or exchange-rate risk
- More straightforward pricing and accounting across EU markets
- Greater appeal to foreign investors
For travelers
- No exchange fees or cash confusion
- Transparent pricing across borders
- Smoother travel within the euro area
Bulgaria’s entry into the euro is a historic turning point. It strengthens EU unity, boosts trade confidence, and signals that economic convergence, while slow, is still moving forward.
Rising Defense Budgets: €381 Billion in EU Spending – Fueling Growth or Straining Resources?
Europe’s security priorities have reshaped its economic agenda. Defense spending across the EU rose from €343.2 billion in 2024 to €381 billion in 2025 and continues to climb into 2026. For the first time in decades, military budgets are no longer a side issue. They are a central pillar of public investment.
Germany sits at the center of this shift. Its €82.69 billion defense budget for 2026 signals a long-term commitment, not a temporary response. Across the bloc, EU countries are now spending an average of 2.04 percent of GDP on defense, aligning more closely with NATO targets and redefining fiscal priorities.
This surge brings apparent economic ripple effects. Defense manufacturing is expanding, especially in aerospace, cybersecurity, drones, and advanced electronics. These sectors create high-skilled jobs and pull investment into regional industrial hubs. Mergers and acquisitions in defense and dual-use technology have accelerated, boosting activity in finance, legal services, and capital markets.
At the same time, the trade-offs are real. Higher defense outlays limit room for social spending, climate programs, and tax relief. Governments face tough choices, especially as debt levels remain elevated in parts of southern Europe. This investment bolsters security but demands careful fiscal balancing.
Where the money is flowing (illustrative breakdown):
- Equipment and weapons systems
- R&D and defense technology
- Personnel and training
- Cyber and intelligence infrastructure
Economic implications to watch:
- Innovation spillovers into civilian tech, especially AI and robotics
- Regional job growth in manufacturing-heavy economies
- Rising defense-linked bonds, attracting institutional investors
In 2026, defense spending is no longer just about protection. It is shaping Europe’s industrial strategy and competitiveness. The challenge is ensuring that security investment strengthens the economy—without crowding out the social and green priorities that also define Europe’s future.
The Deindustrialization Dilemma: 700,000 Jobs Lost in Manufacturing – Threats to Innovation and Employment

Europe’s recovery story has a weak spot. Manufacturing.
Between 2018 and 2024, the EU lost around 700,000 manufacturing jobs, and the decline has not entirely stopped in 2026. Industrial output is still below pre-crisis levels, with a cumulative drop of roughly 5.8 percent across key sectors. For economies built on industrial strength, this trend raises complex questions.
Germany feels the pressure most. High energy costs, slower global demand, and delayed investment have weighed heavily on factories. The result is a sluggish industrial rebound and growing concern about long-term competitiveness. When factories shrink, innovation often follows. Fewer production sites mean fewer testing grounds for new technologies.
The effects ripple outward. Supply chains become thinner and more fragile. Smaller suppliers struggle to survive. Banks and investors reduce exposure to industrial lending, favoring services or real estate instead. Over time, this can lock regions into slower growth paths.
Industries hit hardest include:
- Automotive manufacturing and suppliers
- Basic metals and chemicals
- Energy-intensive heavy industry
- Traditional machinery production
Job losses also deepen skills mismatches. Experienced workers exit the labor market, while younger talent looks elsewhere. Once lost, industrial know-how is complex to rebuild.
Still, deindustrialization is not the end of the story. It is also forcing change. Many firms are shifting toward high-tech manufacturing, automation, and clean production. EU funding now targets advanced batteries, semiconductors, and green steel. As one recent industry report noted, “Europe is not losing industry, it is being forced to reinvent it.”
The risk is delay. Without faster reform, workforce retraining, and energy price stability, Europe could lose both jobs and its capacity for innovation.
The opportunity lies in acting early. Regions that pivot successfully may emerge smaller, but brighter, cleaner, and more competitive.
High-Growth Horizons: €2.2 Trillion in Clean Energy Investments – Green Tech and Productivity Reforms Leading the Charge
If Europe’s old growth engines are slowing, new ones are clearly switching on. Clean energy and productivity reform are now among the continent’s strongest economic drivers.
Globally, clean energy investment reached €2.2 trillion in 2025 and continues to rise in 2026. Europe is capturing a growing share of that capital. Several EU countries are on track to source up to 80 percent of electricity from renewables within the next few years, supported by EU funding, national subsidies, and private investment. By 2030, the global green tech market is projected to reach €12 trillion, placing Europe in a prime position to compete.
This is not just a climate story. It is an economic one.
Renewables, electrification, and AI-driven efficiency are lifting productivity in industries that have stalled. Cheaper renewable power helps stabilize energy costs for businesses. Automation and smart grids reduce waste. Digital tools allow firms to do more with fewer inputs, which is crucial in a tight labor market.
Finance is following fast. Green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, and climate-focused funds are now mainstream investment products. For businesses, access to capital increasingly depends on credible green strategies.
Top growth areas shaping Europe’s economy in 2026:
- Renewable energy
- Solar and offshore wind expansion in Spain, the Nordics, and the North Sea
- Energy storage
- Battery production and grid-scale storage across Germany, France, and Eastern Europe
- Electrification
- EV infrastructure, heat pumps, and industrial electrification
- Green hydrogen
- Heavy industry pilots in steel, chemicals, and shipping
- AI and efficiency tech
- Smart factories, energy management, and predictive maintenance
These sectors offer fertile ground for innovation and returns. They also create high-skilled jobs and help offset losses from deindustrialization.
For investors, workers, and entrepreneurs, the message is clear. Europe’s growth in 2026 may be moderate—but in green tech, it is accelerating fast.
Case Study: Germany’s January 2026 Boost – Minimum Wage Hike to €13.90 and Tax Relief up to €12,348

Germany enters 2026 with a clear message: more money in workers’ pockets, and stronger domestic demand.
From January 2026, the statutory minimum wage will rise to €13.90 per hour, one of the highest in the EU. At the same time, the basic tax-free allowance increases to €12,348, ensuring low- and middle-income earners keep more of what they earn. Combined with average pay rises of around 6 percent, these changes mark a decisive shift in economic policy.
The goal is simple. Support consumption without fueling inflation.
For workers, the impact is immediate. Higher wages and lower tax burdens raise net income, especially for households hit hardest by past price increases. That extra spending power flows quickly into retail, travel, housing, and services, sectors that depend on domestic demand.
For businesses, the picture is mixed. Higher labor costs increase pressure on margins, particularly in hospitality, logistics, and care services. But stronger consumer spending helps offset part of that cost. Firms investing in automation and productivity gains are best placed to adapt.
Germany’s key changes at a glance (2025 → 2026):
- Minimum wage rises to €13.90/hour
- Basic tax allowance increases to €12,348
- Average negotiated wages rise by ~6%
Impact on businesses
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Stronger consumer demand | Higher wage bills |
| More stable workforce | Pressure on low-margin sectors |
| Improved employee retention | Faster need for automation |
These reforms also matter beyond Germany. As Europe’s largest economy, Germany’s wage and tax policies influence regional demand, supply chains, and competitiveness. Higher incomes support imports from neighboring countries, spreading growth across the EU.
These changes signal a worker-friendly shift, fostering economic momentum. For 2026, Germany is betting that fair pay and smart tax relief can strengthen both social stability and financial resilience.
EU Strategies for Competitiveness: Prioritizing Innovation, Decarbonization, and Resilience in 2026
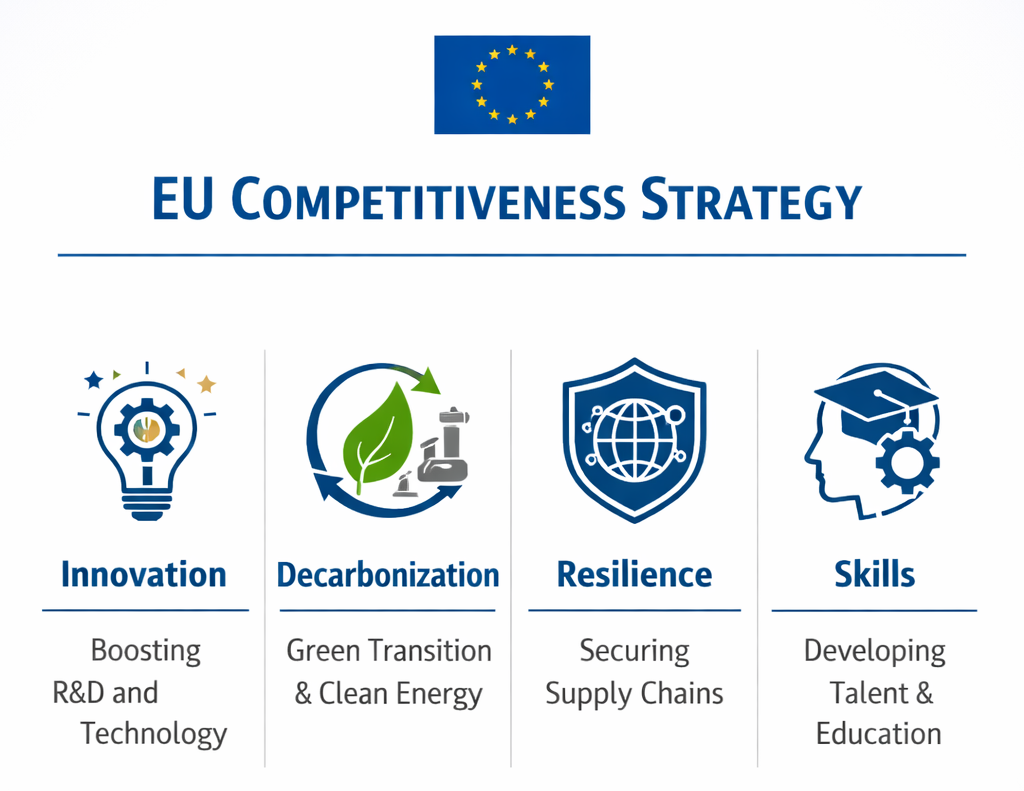
In 2026, Europe’s economic playbook is no longer about short-term fixes. It is about staying competitive in a more challenging global race.
Under the 2026 European Semester, EU leaders have aligned around a clear goal: raise productivity while protecting economic security. The focus is on long-term capacity, how Europe produces energy, builds industry, and finances growth in a more uncertain world.
At the heart of this strategy is investment. The EU is channeling up to €1.5 trillion in green and transition-related funding through public budgets, private capital, and blended finance tools. This push ties directly into earlier trends, defense-driven innovation, green tech expansion, and efforts to counter deindustrialization.
The EU’s 2026 competitiveness pillars include:
- Innovation and productivity
- Scaling AI, automation, and digital infrastructure
- Supporting startups and deep-tech manufacturing
- Decarbonization and electrification
- Expanding renewable power and grid capacity
- Reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels to boost energy autonomy
- Economic security and resilience
- Strengthening critical supply chains
- Investing in semiconductors, batteries, and clean materials
- Skills and workforce adaptation
- Reskilling workers from declining industries
- Aligning education with green and digital jobs
For businesses, these frameworks offer direction and funding clarity. Companies aligned with EU priorities often gain easier access to grants, loans, and public contracts. For investors, the strategy reduces policy risk by signaling where long-term support will remain.
These frameworks equip Europe to thrive in a competitive global landscape. Growth in 2026 may be measured, but it is increasingly strategic—focused on resilience, autonomy, and sustainable advantage rather than speed alone.
Practical Advice: Navigating Investment Hotspots for Entrepreneurs and Travelers
Europe’s 2026 economy rewards focus and timing. Growth is uneven, but clear hotspots are emerging for those willing to plan carefully. Whether you’re investing, hiring, or traveling, the key is aligning your choices with structural trends, not short-term noise.
Consider these steps to capitalize on 2026 trends:
- Look east for euro-stable opportunities
Bulgaria’s eurozone entry removes currency risk and boosts investor confidence. Real estate, logistics, tourism, and outsourcing stand to benefit most. For entrepreneurs, euro pricing simplifies contracts and cross-border payments. - Follow the green energy map.
Portugal, Spain, and parts of the Nordics are fast becoming clean-tech hubs. Portugal already sources around 60 percent of electricity from renewables, with targets rising toward 80 percent. This creates demand for engineers, project managers, and green finance expertise. - Use Germany’s wage growth strategically.
Germany’s higher minimum wage and tax relief make it easier to attract skilled workers. For businesses, this is a chance to recruit talent, especially in tech, engineering, and sustainability, while investing in productivity to offset higher labor costs. - Explore innovation-driven travel and business hubs.
Defense and dual-use tech clusters in Germany, France, and Poland are drawing startups and researchers. Travelers interested in business networking can combine visits with innovation expos, industrial fairs, or university-led research centers. - Be cautious in deindustrialization-affected regions.
Areas losing traditional manufacturing jobs may offer lower costs, but also higher risk. Look for places with active retraining programs, EU funding, or green reindustrialization plans before committing capital or relocating.
Quick Due Diligence Checklist for 2026
- Is the region aligned with EU green or innovation funding?
- Are labor and energy costs predictable over the next 3–5 years?
- Does eurozone membership reduce financial risk?
- Are local skills evolving, or declining?
- Is demand driven by long-term policy, not short-term incentives?
Europe’s economy in 2026 favors those who prepare. With the proper checks in place, today’s cautious landscape can become tomorrow’s opportunity.
Conclusion: Embracing Opportunities in a Dynamic Year
Europe is turning global collaboration into impactful science.
— European Commission (@EU_Commission) December 14, 2025
In 2026-2027, Horizon Europe is investing €14 Bn in clean tech, to advance healthcare via ethical AI, boost jobs by backing innovators, and tackle challenges that matter.
More info ↓https://t.co/bP9H6rGF3e pic.twitter.com/AGLISlPPn1
Europe’s economic outlook in 2026 is neither a warning sign nor a victory lap. It is a moment of transition.
Growth remains modest, shaped by global uncertainty, deindustrialization pressures, and tighter fiscal choices. Yet the opportunities are clear. Bulgaria’s eurozone entry strengthens integration. Defense spending is reshaping industrial capacity. Green tech and productivity reforms are opening new paths for investment and jobs. In Germany, higher wages and tax relief are reinforcing domestic demand and labor stability.
The common thread is direction. Europe is no longer reacting; it is repositioning.
For entrepreneurs, investors, and travelers, 2026 rewards informed decisions—target regions aligned with EU funding. Watch where innovation and skills are clustering. Plan for stability, not speculation.
With strategic choices, Europe could accelerate growth beyond current projections. The foundations are already in place.
This is a year to stay engaged. Economic signals will evolve, and new opportunities will emerge. Keep an eye on policy shifts, investment flows, and regional success stories, because Europe’s economic horizon is still unfolding.
